|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|


A construction project involve varied multi-dimensional activities from surveys, pre-construction to completion of the project. These activities are project planning and designing, construction stages outlining, time scheduling, financial arrangements, material management, construction equipment mobilization, technical coordination with agencies, sub-contracting, manpower management, quality checks & approvals, construction safety, consumables and resource arrangements etc.
Successful completion of the project according to the contract terms require logical planning and implementation of these simultaneous activities. The present-day mega projects are aided and managed by advanced digital computations like BIM, MSP, Primavera, PowerBI, etc.



Building repairs and renovations involve restraining building components and structural elements from aging deterioration, increase its life and safety, and renew it with improved serviceability, functionality and aesthetics. A systematic approach for this includes inspection and analysis of the structural damage, work out an appropriate repairing method, updating building systems, and enhancing interior and exterior features. Renovations also include upgrading the electrical, plumbing, insulation, windows and roofing for enhancing their service efficiency, as well as modernizing the building with latest technology to equip it for upscaling life styles and utility. Repairs address issues such as leaks, cracks, and deterioration to maintain structural integrity and prevent further damage.
A professional assessment and planning ensure compliance with building codes and regulations while meeting the needs and preferences of occupants. Ultimately, building repairs and renovations enhance property value, comfort in terms of building services and sustainability for present and future occupants.


Building systems assessment involves evaluating the performance, efficiency, and functionality of the building’s installed service systems as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, plumbing, electrical and safety systems. This assessment aims to identify scopes for improvement, energy conservation, and cost savings while ensuring occupant comfort and safety. Energy audits, building performance evaluations, and predictive maintenance techniques are used to analyse system operation, identify inefficiencies, and prioritize upgrades or retrofits.
By assessing building systems, owners and managers can optimize resource utilization, enhance sustainability, comply with regulations, and prolong the lifespan of infrastructure ultimately fostering healthier, more efficient, and resilient built environments.
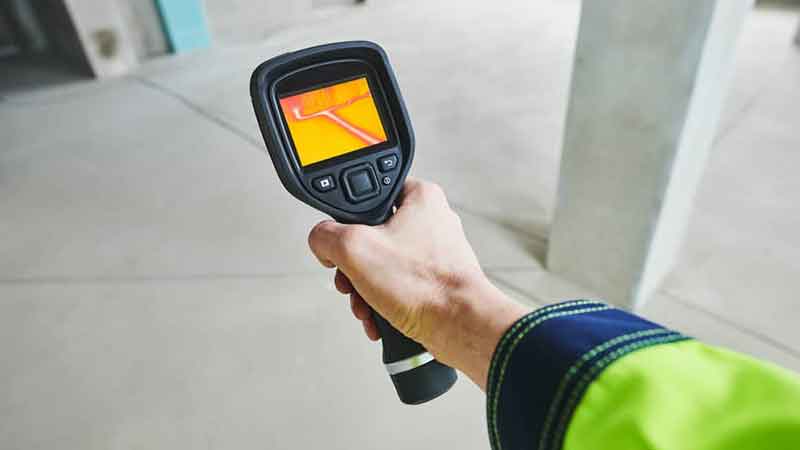
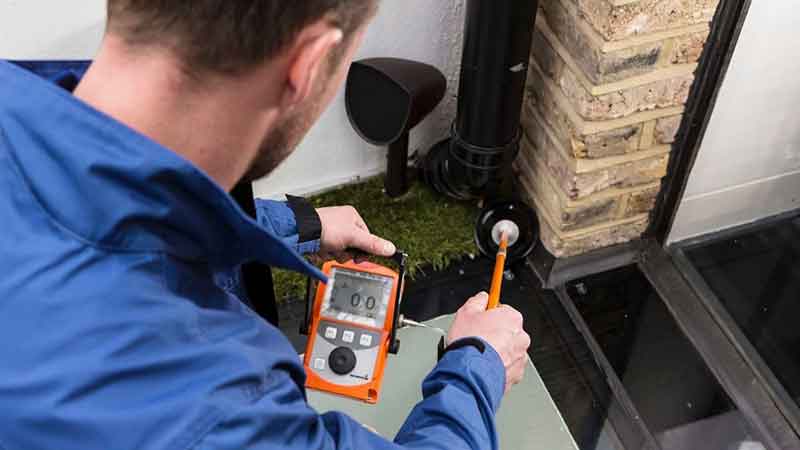


Water leakages and its subsequent penetrations in the buildings cause deterioration and irreversible damage to the structures. Water seepages causes spalling of concrete and weakens the bonding within structural elements and other building components. Water leaks and seepage are the major cause for weakening the building structure and reducing life span of the building. Apart from these, water seepages leads to mould and mildew growths resulting in unhygienic and unhealthy indoor environments. Water leaks & seepages must be detected and resolved in time with proper solution to stop further deterioration of the building.
Remote scanning is a trustworthy method in the form of non-destructive investigation to locate the likely point of water leakage in the building. It analyses the temperature differences in the structural elements and convert them into adaptable moisture concentrations that provides fair information about the source of water seepage and its spread. This scanning further directs the process of actual rectification or repair works to be performed for stopping the leakages.
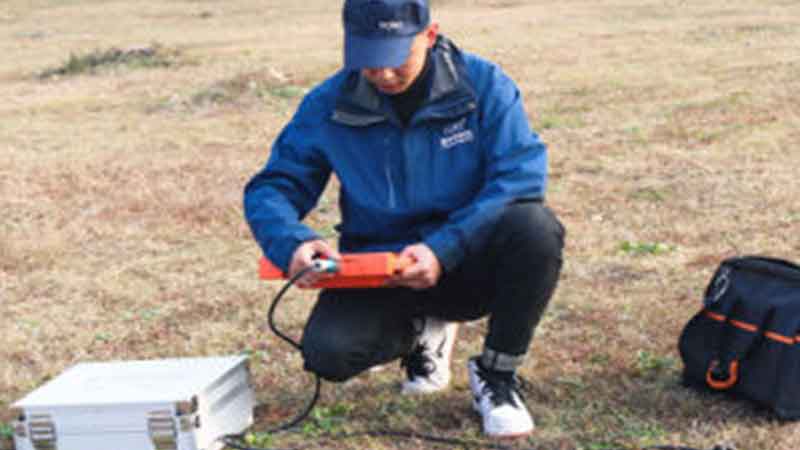
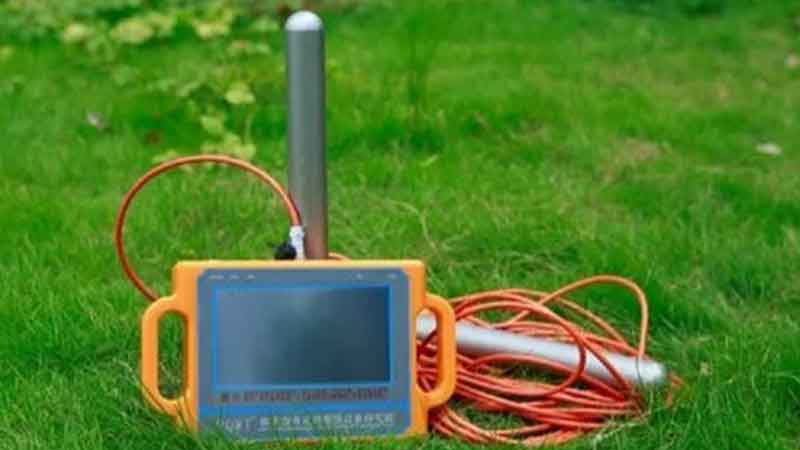


Ground water is the most essential natural resource that is undergoing depletion year by year. Everywhere the ground water table is deepening, posing a threat for availability of this precious resource. Per capita availability of water as a natural resource is reducing at an alarming rate. It is the foremost requirement for the humanity to identify its underground location in a scientific manner to reduce the exploration costs and save other natural resources, and use this resource very thoughtfully.
Ground water availability is examined by geophysical and remote sensing methods using parameters like density, velocity, conductivity & resistivity, magnetic, electromagnetic and radioactive phenomena.
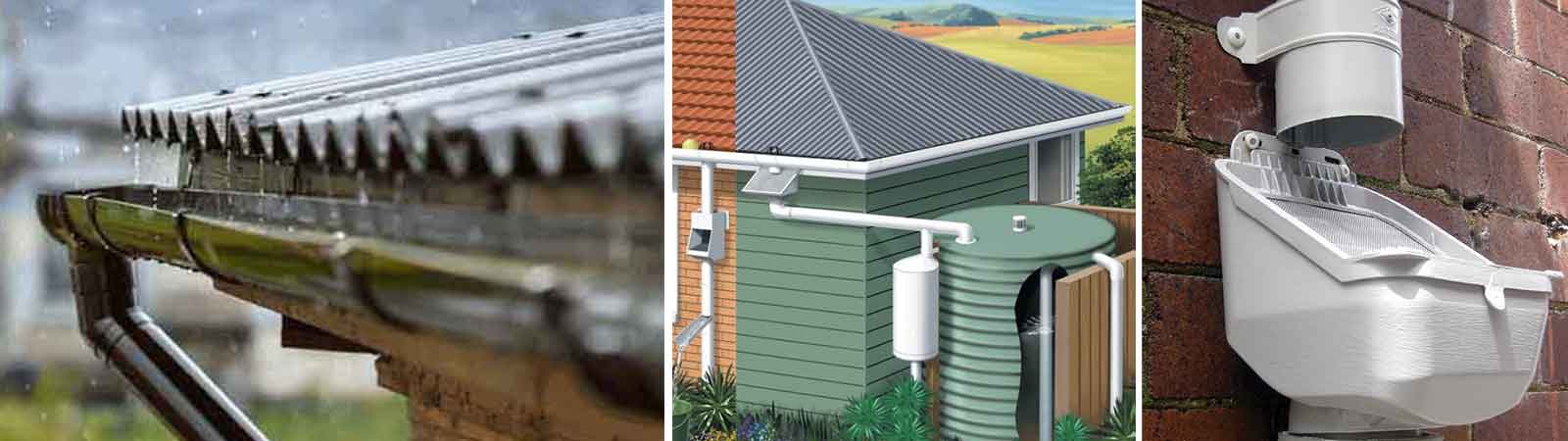
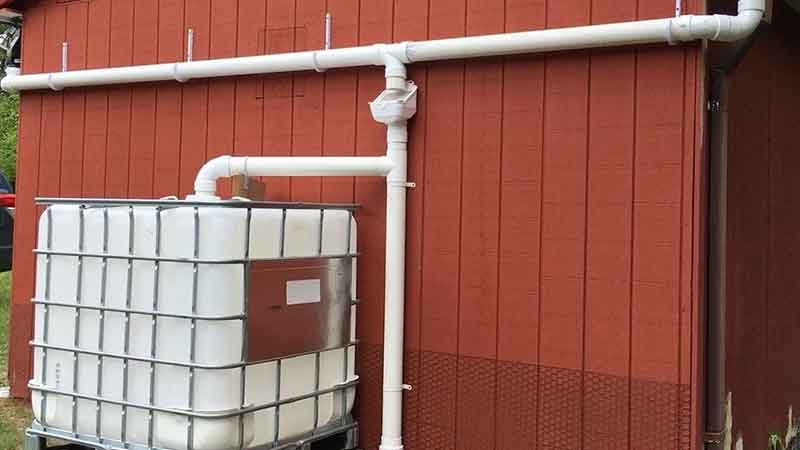
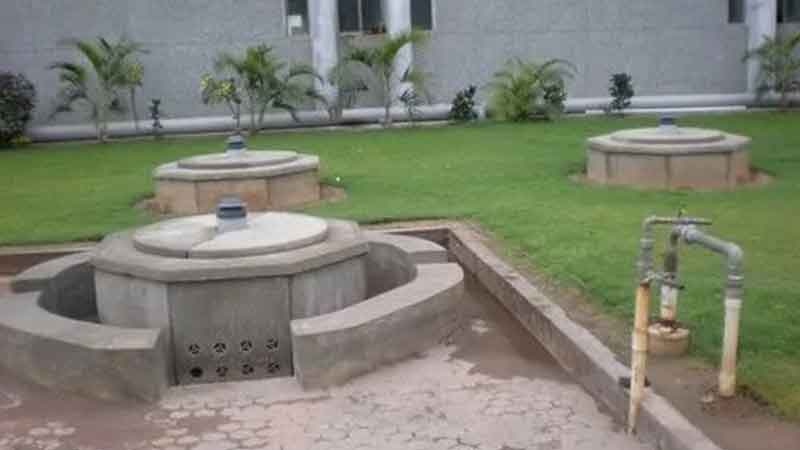



Rainwater harvesting is a very practical solution to conserve the natural water received as ‘rainwater’. It is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for various purposes such as irrigation, domestic use, and groundwater recharge This stored rainwater can be used for non-potable purposes like gardening, toilet flushing, and washing; thereby reducing dependence on freshwater sources, mitigating water scarcity and promoting sustainable water management, especially in regions facing water shortages or erratic rainfall patterns.
Consequently, rainwater harvesting alleviates civic authorities’ pressure of community water supplies, conserves energy associated with water treatment, reduces runoff and minimize soil erosion & flooding risks.
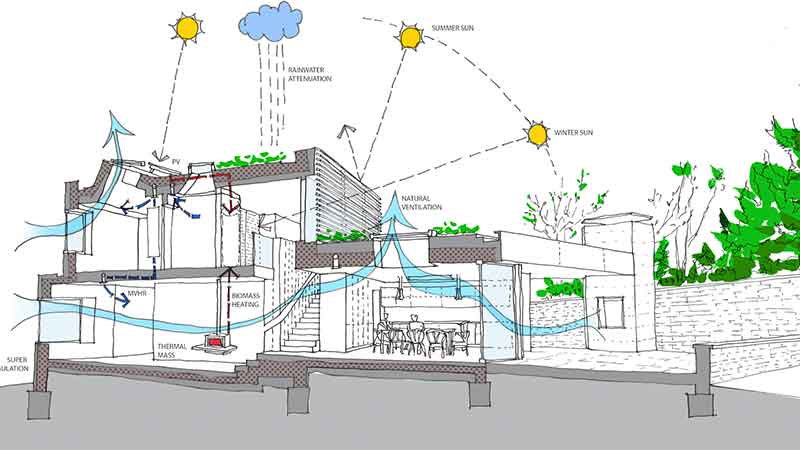

The built environment (a building) has both positive and negative effects on the natural environment, as well as on health of the people using the building. Green building is an all-inclusive effort to increase the positive effects and reduce the negative effects throughout the entire life cycle of the building. The basic approach for Green Building lies in planning, design, construction, and operations (service or use) of buildings targeting energy and natural resources conservation.
The broad spectrum of green buildings spans into Planning and site selection, Water efficiency, Energy efficiency, Materials, Waste reduction and management, Indoor environmental quality and Design innovation. The green building aspect and implementations are rising with the need of environmental sustainability and is largely promoted by governing bodies and councils.
Green building practices substantially mitigate the negative environmental impacts and also paves the way for improving the existing buildings design, construction and operational practices. As an added benefit, green design measures reduce operating costs, enhance building marketability and increase occupants’ productivity.
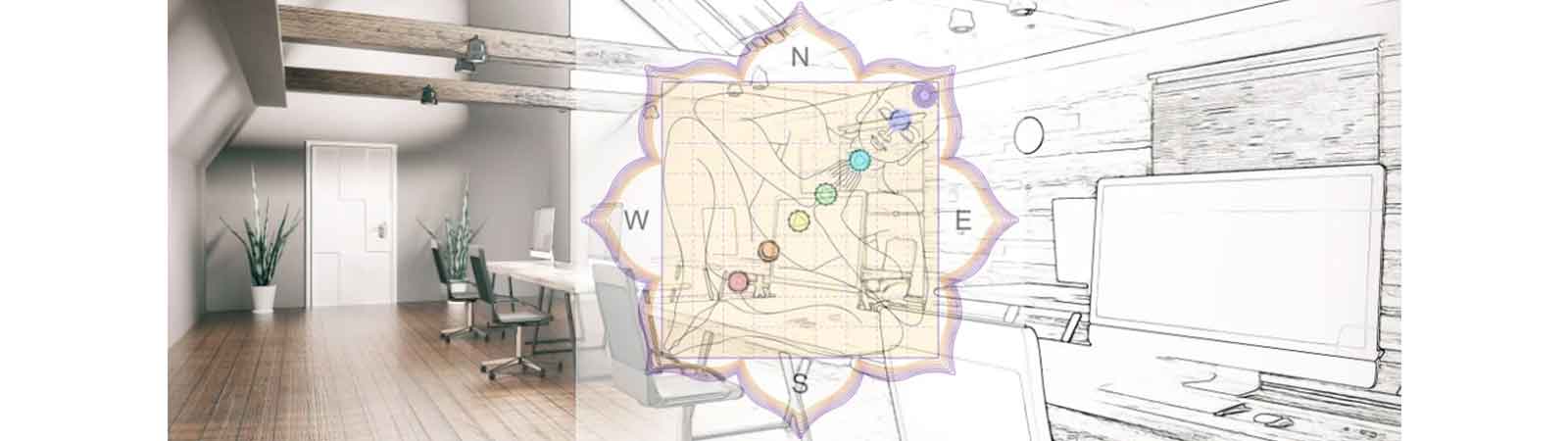
Vastu Shastra: The basic Indian science integrating construction aspects with nature; related to orientation, layout, and design of buildings with an aim to create spiritual harmony and get benefits of the natural powers for enhanced health, wealth, prosperity and happiness in home and work places. It is a scientific approach that considers various factors as Sun's effects, Earth's magnetic field, Winds, topography, nearby structures, and natural elements and their effects on building and its occupants.

Regulatory compliance of an organization establishes its legality and ethical practices. This prevents penalties, fines, or potential shutdowns due to non-compliance while fostering a culture of integrity, transparency, and accountability. Compliance also helps to mitigate risks, provides employees a safe workplace, reduces environmental impact, protect consumers and prevent data breaches; enhancing the brand reputation and making business sustainable.
Regulatory compliance specialists examine and investigate eligibility for or in conformity with the rules and regulations of the governing body, carry out other compliance and enforcement inspection, analyse and prepare documentation for submissions for their approvals.
